Fatty Liver Causes & Symptoms 8 Natural treatments And Best Exercise For Fatty Liver
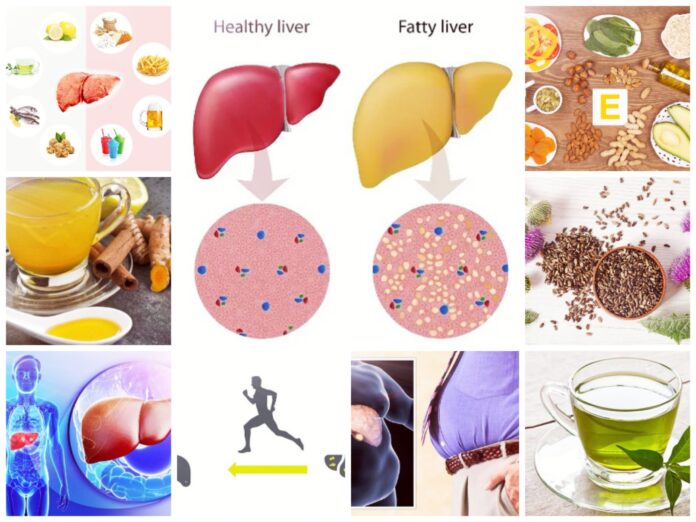
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. The condition is commonly associated with alcoholism, but it can also occur in non-drinkers. Fatty liver disease can lead to severe liver damage if not diagnosed and treated early. In this article, we will discuss what fatty liver is, its symptoms, and its causes.
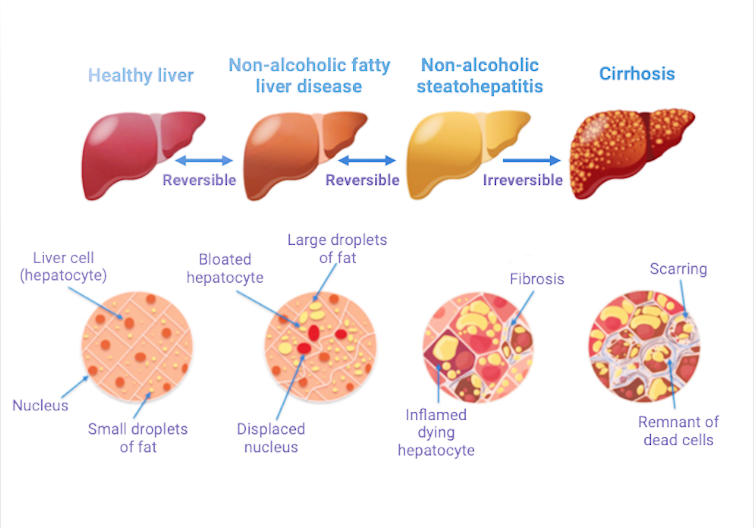
What is Fatty Liver? The liver is a vital organ in the body responsible for processing nutrients, filtering toxins, and producing bile. When there is an accumulation of fat in the liver, the organ becomes heavier and increases in size. This buildup of fat is known as fatty liver or hepatic steatosis. Fatty liver is a reversible condition, and with appropriate treatment, it can be resolved. However, if left untreated, it can progress to more severe liver diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
There are two types of fatty liver disease:
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease:
This type of fatty liver disease is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol is metabolized in the liver, and when consumed in large amounts, it causes the liver to become overwhelmed and unable to metabolize it effectively. This leads to the accumulation of fat in the liver.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: This type of fatty liver disease occurs in individuals who do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol. It is the most common form of fatty liver disease, and it is often associated with obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease can be further classified into two categories:a. Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL): In this type of fatty liver disease, the accumulation of fat in the liver is not accompanied by inflammation or liver damage. b.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): In this type of fatty liver disease, the accumulation of fat in the liver is accompanied by inflammation and liver damage. NASH can lead to more severe liver diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver: Fatty liver disease is often asymptomatic, meaning that individuals with the condition may not experience any symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, some symptoms may become apparent. The symptoms of fatty liver disease include:
Fatigue: Individuals with fatty liver disease may experience fatigue or weakness due to the accumulation of fat in the liver, which can impair liver function.
Abdominal discomfort: Some individuals with fatty liver disease may experience discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen due to an enlarged liver.
Jaundice: In severe cases, fatty liver disease can cause jaundice, a condition in which the skin and eyes turn yellow due to a buildup of bilirubin in the blood.
Spider angiomas: Spider angiomas are small, spider-like blood vessels that can appear on the skin due to liver damage caused by fatty liver disease.
Enlarged liver: Fatty liver disease can cause the liver to become enlarged, which can be detected through a physical examination or imaging tests such as an ultrasound.
Elevated liver enzymes: Individuals with fatty liver disease may have elevated levels of liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), in their blood.
Causes of Fatty Liver: The exact cause of fatty liver disease is not known, but several factors can contribute to its development. These factors include:
Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is a leading cause of fatty liver disease. Alcohol is metabolized in the liver, and when consumed in large amounts, it causes the liver to become overwhelmed and unable to process it effectively, leading to the accumulation of fat in the liver.
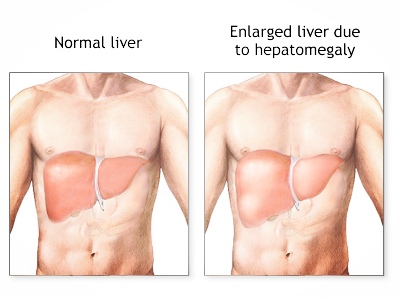
Obesity: Obesity is another significant risk factor for liver fat, as excess body fat can lead to the buildup of fat in the liver.
Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance, which is commonly associated with type 2 diabetes, can also contribute to the development of liver fat.
High cholesterol and triglycerides: High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can contribute to the accumulation of fat in the liver.
Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, tamoxifen, and methotrexate, can cause fatty liver disease as a side effect.
Genetics: Some individuals may be more prone to developing the fatty liver disease due to their genetics.
Rapid weight loss: Rapid weight loss, especially through crash diets, can also cause liver fat.
Other health conditions: Other health conditions, such as metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and sleep apnea, can also increase the risk of developing liver fat.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Fatty Liver:Fatty liver disease is often diagnosed through imaging tests such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. Blood tests may also be used to check for elevated liver enzymes and other signs of liver damage. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of liver damage.
Treatment for fatty liver disease depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In cases of alcoholic liver fat, the most effective treatment is to stop drinking alcohol. In non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, lifestyle changes such as weight loss, regular exercise, and a healthy diet can be effective in reducing liver fat and improving liver function.
In cases of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), additional medical treatment may be necessary to reduce inflammation and prevent liver damage.
This may include medications such as vitamin E, pioglitazone, or obeticholic acid, which are effective in reducing liver inflammation and fibrosis. In severe cases of fatty liver disease, where the liver has been significantly damaged, a liver transplant may be necessary.
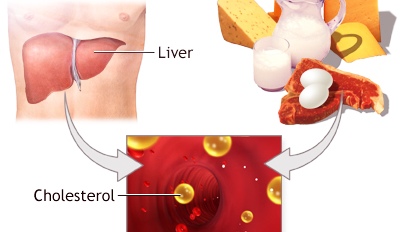
Prevention of Fatty Liver: Fatty liver disease can be prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding medications that can cause liver damage. Individuals with diabetes or high cholesterol should work with their healthcare provider to manage these conditions and reduce their risk of developing liver fat.
In addition to medical treatments, some natural home remedies may help in managing liver fat. Here are some examples:
Diet modifications: A healthy diet can play a crucial role in managing liver fat. It is recommended to avoid saturated and trans fats, processed foods, and sugar, and consume more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Additionally, increasing fiber intake and drinking plenty of water can also be beneficial.
Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve liver function and reduce liver fat. It is recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Weight loss: Losing weight can help reduce liver fat and improve liver function. A gradual weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week is recommended to avoid rapid weight loss, which can worsen liver fat.
Green tea: Green tea contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that may help reduce liver inflammation and improve liver function.
Milk thistle: Milk thistle is a herb that has been used for centuries to treat liver problems. It contains a compound called silymarin, which has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce liver inflammation and improve liver function.
Turmeric: Turmeric contains a compound called curcumin, which has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce liver inflammation and improve liver function.
Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish such as salmon and tuna, may help reduce liver inflammation and improve liver function.
Vitamin E: Vitamin E is an antioxidant that may help reduce liver inflammation and improve liver function. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements, as high doses of vitamin E can be harmful.
It is important to note that these natural remedies should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment, but rather as a complementary approach to managing liver fat. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment or supplement.
In conclusion, fatty liver disease is a common condition that can lead to severe liver damage if not diagnosed and treated early. The condition is often asymptomatic, but symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and jaundice may become apparent as the disease progresses. liver fat can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, insulin resistance, and certain medications. Treatment for liver fat depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition and may include lifestyle changes, medications, or a liver transplant in severe cases. Preventative measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can reduce the risk of developing liver fat.
The best exercises for fatty liver
Regular exercise is an important part of managing liver fat. Exercise can help reduce liver fat, improve liver function, and reduce the risk of developing other health conditions that can contribute to fatty liver diseases, such as obesity and insulin resistance. Here are some of the best exercises for fatty liver disease:
Aerobic exercise: Aerobic exercise, also known as cardio exercise, is any exercise that raises the heart rate and increases the breathing rate. Examples of aerobic exercise include brisk walking, running, cycling, swimming, and dancing. Aerobic exercise is s effective in reducing liver fat and improving liver function.
Resistance training: Resistance training, also known as strength training or weightlifting, involves using weights or resistance bands to strengthen and build muscle. Resistance training can help improve insulin sensitivity, which is important for managing liver fat. Additionally, building muscle can help increase metabolism and reduce body fat.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT): HIIT involves alternating between periods of high-intensity exercise and periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. HIIT is effective in reducing liver fat and improving liver function. Examples of HIIT workouts include sprint intervals, jump rope intervals, and circuit training.
Yoga: Yoga is a gentle form of exercise that combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation. Yoga is effective in reducing liver fat and improving liver function. Additionally, yoga can help reduce stress, which is important for managing this disease.
Pilates: Pilates is a low-impact form of exercise that focuses on strengthening the core muscles and improving posture. Pilates is effective in reducing liver fat and improving liver function.
It is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise to avoid injury. It is also recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have other health conditions or concerns.