Vitamin d deficiency symptoms cause and Vitamin D Deficiency Effects On The Body And Natural Treatment
Here are some common symptoms of vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays many important roles in the body, including maintaining strong bones and supporting a healthy immune system. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to a deficiency, which can cause a range of symptoms and health problems.
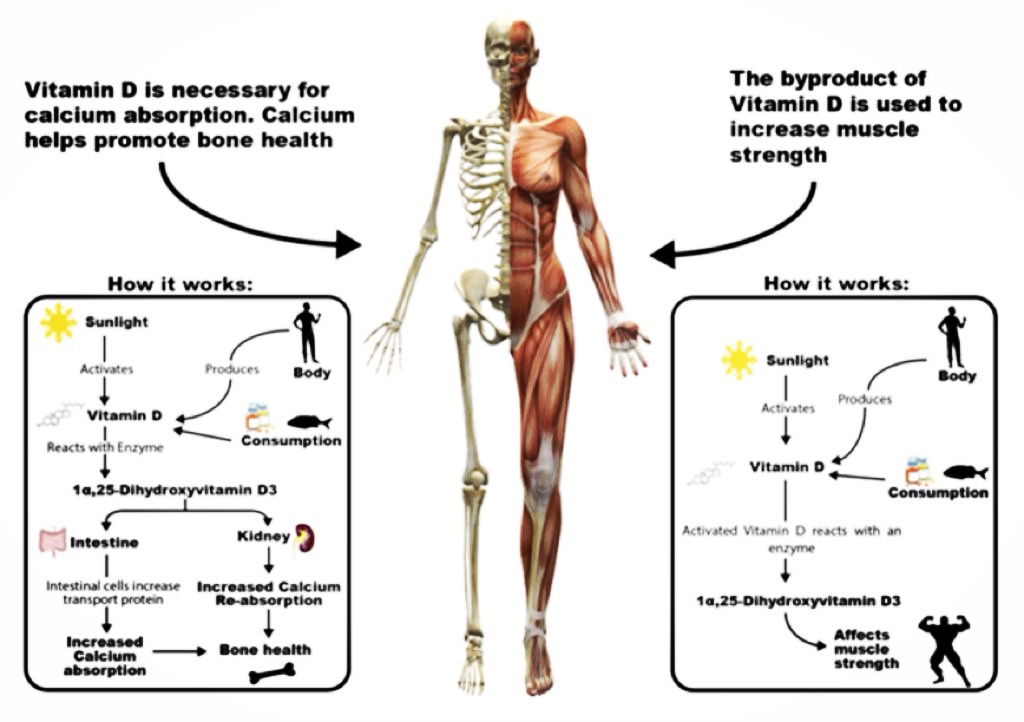
Bone pain and muscle weakness: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is essential for building and maintaining strong bones. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to weak bones and muscles, which can cause pain and weakness.
Fatigue and weakness: Vitamin D deficiency can cause general fatigue and weakness, which can make it difficult to perform daily tasks.
Depression and mood changes: Studies have linked vitamin D deficiency to an increased risk of depression and other mood disorders.
Impaired wound healing: Vitamin D plays a role in the body’s immune response, and a deficiency can lead to impaired wound healing and a higher risk of infection.
Hair loss: Some studies have suggested that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to hair loss, although more research is needed to confirm this association.
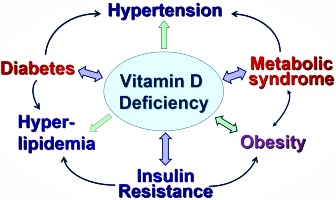
Increased risk of certain health problems: Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of several health problems, including osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
Weight gain: While vitamin D deficiency does not directly cause weight gain, it has been linked to obesity. Some studies suggest that vitamin D may play a role in regulating metabolism and body weight, and a deficiency in vitamin D may contribute to weight gain.
Muscle cramps: Vitamin D is important for maintaining muscle health and strength, and a deficiency can lead to muscle weakness and cramps.
Back pain: Vitamin D is important for bone health, and a deficiency can lead to weakened bones and muscles, which can cause back pain.
Sleep changes: Vitamin D is important for regulating the body’s circadian rhythm, which helps to regulate sleep. A deficiency in vitamin D may affect this process and lead to changes in sleep patterns.
Frequent cough and cold: Vitamin D plays a role in supporting a healthy immune system, and a deficiency can increase the risk of respiratory infections like cold and flu.
Pale skin and dark circles: Vitamin D deficiency can affect the body’s ability to absorb calcium, which can lead to weakened bones and teeth. This can cause pale skin and dark circles around the eyes, which can be a sign of weak bones in the face.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other medical conditions, and a diagnosis of vitamin D deficiency should be made by a healthcare provider through a blood test. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider, who can help determine the cause and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Vitamin D Deficiency Effects On The Body And Natural Treatment
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of our bones, muscles, and immune system. It helps the body absorb calcium, which is necessary for the growth and maintenance of strong bones. Vitamin D also supports muscle function and helps reduce inflammation in the body. Additionally, recent studies have shown that vitamin D may play a role in regulating blood pressure, insulin sensitivity, and even mood.
Unfortunately, many people are deficient in this vital nutrient. In fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about one-third of the population in the United States has a vitamin D deficiency. This deficiency can have significant effects on many parts of the body.
Skeletal System: One of the most well-known roles of vitamin D is its role in maintaining the health of our bones. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can’t absorb calcium efficiently, which can lead to weak bones and an increased risk of fractures. In children, a severe vitamin D deficiency can cause a condition called rickets, which causes the bones to become soft and bend. In adults, vitamin D deficiency can lead to osteomalacia, a condition where the bones become weak. This can cause bone pain, muscle weakness, and an increased risk of fractures.
Muscular System: Vitamin D plays a significant role in the functioning of our muscles. It helps regulate muscle contraction and relaxation and is essential for muscle strength. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to muscle weakness, aches, and cramps. In addition to this, vitamin D deficiency can also lead to a condition called myopathy, which is a disorder that affects the muscles’ ability to function correctly. This can cause muscle weakness and pain and can affect a person’s ability to carry out daily activities.
Immune System: Vitamin D also plays a crucial role in the functioning of our immune system. It helps the body produce antimicrobial peptides, which are essential for fighting off infections and diseases. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to a weakened immune system and an increased risk of infections and illnesses. Recent studies have also shown that vitamin D may play a role in reducing the risk of autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Cardiovascular System: Recent studies have suggested that vitamin D may play a role in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. It helps regulate blood pressure and may help reduce the risk of developing heart disease. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to hypertension (high blood pressure), which is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Vitamin D deficiency has also been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks and stroke.
Respiratory System: Vitamin D may also play a role in maintaining a healthy respiratory system. Studies have shown that vitamin D may help reduce the risk of respiratory infections, such as the flu and pneumonia. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to an increased risk of respiratory infections and illnesses.
Endocrine System: Vitamin D is also essential for the functioning of our endocrine system. It helps regulate insulin levels and may help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to insulin resistance, which is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
Nervous System: Recent studies have suggested that vitamin D may play a role in maintaining a healthy nervous system. It helps regulate the production of neurotransmitters, which are essential for brain function. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to an increased risk of developing neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Mental Health: Vitamin D may also play a role in maintaining good mental health. Studies have shown that vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. Some studies have suggested that vitamin D supplementation may be an effective treatment for depression. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Reproductive System: Vitamin D may also play a role in maintaining a healthy reproductive system. Studies have shown that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to fertility problems in both men and women. In men, vitamin D deficiency has been linked to low sperm count and decreased sperm motility. In women, vitamin D deficiency may be linked to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and other fertility problems.
Skin Health: Vitamin D may also play a role in maintaining healthy skin. It helps regulate the production of sebum, which is the oil that keeps our skin moisturized. When the body doesn’t get enough vitamin D, it can lead to skin problems, such as dryness, eczema, and psoriasis.
How to Get Enough Vitamin D: The best way to get enough vitamin D is through exposure to sunlight. When UVB rays from the sun hit the skin, the body produces vitamin D. However, many factors can affect the body’s ability to produce vitamin D through sunlight exposure. These include:
Time of day: The body produces more vitamin D when the sun is high in the sky (between 10 am and 3 pm). Season: The body produces more vitamin D during the summer months when there is more sunlight.
Skin color: People with darker skin produce less vitamin D than people with lighter skin.
Age: As we age, our skin becomes less efficient at producing vitamin D. For these reasons, many people may need to get vitamin D through other sources, such as food and supplements.
While getting enough vitamin D through sunlight exposure, diet, and supplements is the most effective way to prevent vitamin D deficiency, there are also natural remedies that may help support healthy vitamin D levels in the body. Here are a few natural remedies to consider:
Increase sun exposure: Spending more time in the sun during peak hours (between 10 am and 3 pm) can help the body produce more vitamin D. However, it’s important to protect the skin from sunburn and damage by using sunscreen or covering it up with clothing or hats.
Eat vitamin D-rich foods: Incorporating more vitamin D-rich foods into your diet can help increase your vitamin D levels. Some good food sources of vitamin D include fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods like milk and cereal.
Take supplements: Vitamin D supplements can be an effective way to increase your vitamin D levels. However, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplements, as high doses of vitamin D can be toxic.
Get regular exercise: Regular exercise can help improve overall health, including vitamin D levels. Some studies have suggested that weight-bearing exercise may help increase bone density and improve vitamin D levels in the body.
Manage stress: Stress can hurt overall health, including vitamin D levels. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help improve overall health and support healthy vitamin D levels.
It’s important to note that natural remedies should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. If you’re concerned about your vitamin D levels, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider, who can perform a blood test to determine if you’re deficient and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Conclusion: Vitamin D deficiency can affect every part of the body, from the bones and muscles to the immune and nervous systems. It’s important to make sure that you’re getting enough vitamin D through sunlight exposure, diet, or supplements to maintain your overall health. If you’re concerned about your vitamin D levels, talk to your healthcare provider, who can perform a blood test to determine if you’re deficient and recommend the appropriate treatment.

















