Obesity Linked to Cancers.
Obesity Linked to 10 Cancers
Obesity is a major public health problem that affects millions of people worldwide. Obesity Linked to 10 Cancers can lead to a wide range of health problems, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and some cancers. Obesity has been linked to at least 10 types of cancer, making it one of the leading preventable causes of cancer.
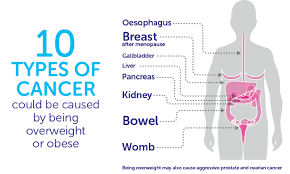
The link between obesity and cancer has been extensively studied in recent years, and the evidence is clear: people who are obese are at a higher risk of developing certain types of cancer. The following are 10 cancers that have been linked to obesity:
Breast cancer: Obesity Linked to 10 Cancers include breast cancer, especially in postmenopausal women. This is because fat tissue produces estrogen, which can promote the growth of breast cancer cells.
Colorectal cancer:
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of colon and rectal cancer. This is because excess body fat can cause inflammation and insulin resistance, which can promote the development of cancer cells.
Endometrial cancer:
Obesity is a significant risk factor for endometrial cancer, as fat tissue produces estrogen, which can cause the lining of the uterus to grow excessively.
Kidney cancer:
Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of kidney cancer, possibly due to hormonal imbalances caused by excess body fat.
Liver cancer:
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of liver cancer, possibly because it can cause inflammation and damage to the liver.
Ovarian cancer:
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer, possibly due to hormonal imbalances caused by excess body fat.
Pancreatic cancer:
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of pancreatic cancer, possibly because it can cause inflammation and damage to the pancreas.
Prostate cancer:
Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer, possibly due to hormonal imbalances caused by excess body fat.
Stomach cancer:
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer, possibly due to the chronic inflammation and metabolic changes caused by excess body fat.
Thyroid cancer:
overweight is linked to an increased risk of thyroid cancer, possibly because excess body fat can cause hormonal imbalances.
Aside from these Obesity Linked to 10 Cancers, obesity has also been linked to an increased risk of other health complications such as:
Type 2 diabetes:
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, as excess body fat can cause insulin resistance, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Cardiovascular disease:
overweight is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, as excess body fat can cause high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and inflammation, all of which can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Sleep apnea: Obesity is a significant risk factor for sleep apnea, a condition in which breathing is interrupted during sleep. This is because excess body fat can obstruct the airways, making it difficult to breathe properly during sleep.
Joint problems
: overweight is linked to an increased risk of joint problems such as osteoarthritis, as excess body weight puts additional stress on the joints.
Gallbladder disease:
overweight is a significant risk factor for gallbladder disease, as excess body fat can cause the liver to produce more cholesterol, which can lead to the formation of gallstones.
Fatty liver disease:
Overweight is linked to an increased risk of fatty liver disease, a condition in which excess fat accumulates in the liver. This can cause inflammation and damage to the liver, and may eventually lead to cirrhosis.
Infertility:
Overweight is a significant risk factor for infertility, as excess body fat can disrupt hormonal balances and interfere with reproductive function.
Additionally, Overweight has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer treatment complications, such as:
Chemotherapy complications: Obese cancer patients may have a higher risk of complications from chemotherapy treatment due to their altered metabolism and immune function.
Radiation therapy complications:

Overweight can make it more difficult to accurately target radiation therapy, as excess body fat can cause shifts in the position of organs and tissues.
Surgical complications:
Overweight cancer patients may have a higher risk of surgical complications due to the increased strain on the body during surgery, as well as the increased risk of infections and wound healing issues.
Furthermore, Overweight can have significant social and psychological consequences, including:
Stigma and discrimination:
Overweight is often stigmatized in society, which can lead to discrimination and lower quality of life for obese individuals.
Depression and anxiety:
Overweight has been linked to an increased risk of depression and anxiety, possibly due to the social stigma and physical limitations associated with obesity.
Reduced quality of life:
Overweight can significantly reduce an individual’s quality of life, as it can limit mobility, cause discomfort, and make everyday activities more difficult.
Overall, overweight is a complex and multifactorial problem that can have significant health, social, and psychological consequences. The link between overweight and cancer, in particular, underscores the importance of promoting healthy lifestyle habits, including regular physical activity and a balanced diet, to prevent and manage overweight and its related health complications. In addition, healthcare providers must also work to address the stigma and discrimination associated with obesity, to ensure that obese individuals receive the support and care they need to maintain their health and well-being.
Overweight is a growing problem worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight in 2016, with more than 650 million of those classified as obese. In addition, more than 340 million children and adolescents aged 5-19 were overweight or obese in 2016. These numbers are expected to continue to rise, with obesity rates projected to increase to 18% of men and over 21% of women by 2025.
The causes of overweight are complex and multifactorial, involving a combination of genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors. In general, Overweight occurs when energy intake (calories consumed) exceeds energy expenditure (calories burned), leading to excess body fat accumulation. This can be influenced by a variety of factors, including:
Genetics:
Certain genetic factors may make individuals more susceptible to overweight , by influencing appetite, metabolism, and fat storage.
Environmental factors:
Environmental factors, such as access to high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, sedentary lifestyles, and lack of access to safe and affordable physical activity opportunities, can also contribute to Overweight .
Behavioral factors:
Behavioral factors, such as overeating, lack of physical activity, and poor sleep habits, can also contribute to Overweight .
Medical conditions:
Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism and Cushing’s syndrome, can also contribute to Overweight .
Preventing and managing obesity requires a multifaceted approach that involves addressing these underlying factors. This may include:
Promoting healthy lifestyle habits:
Encouraging regular physical activity, healthy eating habits, and good sleep hygiene can help prevent and manage overweight .
Providing education and support:
Providing education and support to individuals and communities on healthy lifestyle habits can help promote long-term behavior change.
Creating supportive environments: Creating supportive environments that promote healthy behaviors, such as access to safe and affordable physical activity opportunities and healthy food options, can also help prevent and manage overweight .
Addressing medical conditions: Addressing underlying medical conditions that contribute to obesity, such as hypothyroidism or Cushing’s syndrome, can also be an important part of managing overweight .
Psychological support:
Providing psychological support to individuals who are struggling with obesity can help address the emotional and social consequences of obesity and may help promote long-term behavior change.
In conclusion, overweight is a major public health problem that is associated with a range of health complications, including cancer. The link between obesity and cancer underscores the importance of promoting healthy lifestyle habits and creating supportive environments that promote healthy behaviors. By addressing the underlying factors that contribute to obesity, and providing education, support, and access to resources, we can work to prevent and manage obesity and its related health complications.